하기 전에 잠깐 네트워크 연결 하는 방법



오늘은 깃을 통해서 작업일 해볼꺼




도망 칠때는 :q!
의도해서 저장하고 싶을 때 wq
apt-get 이용하기
apt : Advanced Package Tool 의 약자

루프 /설킷
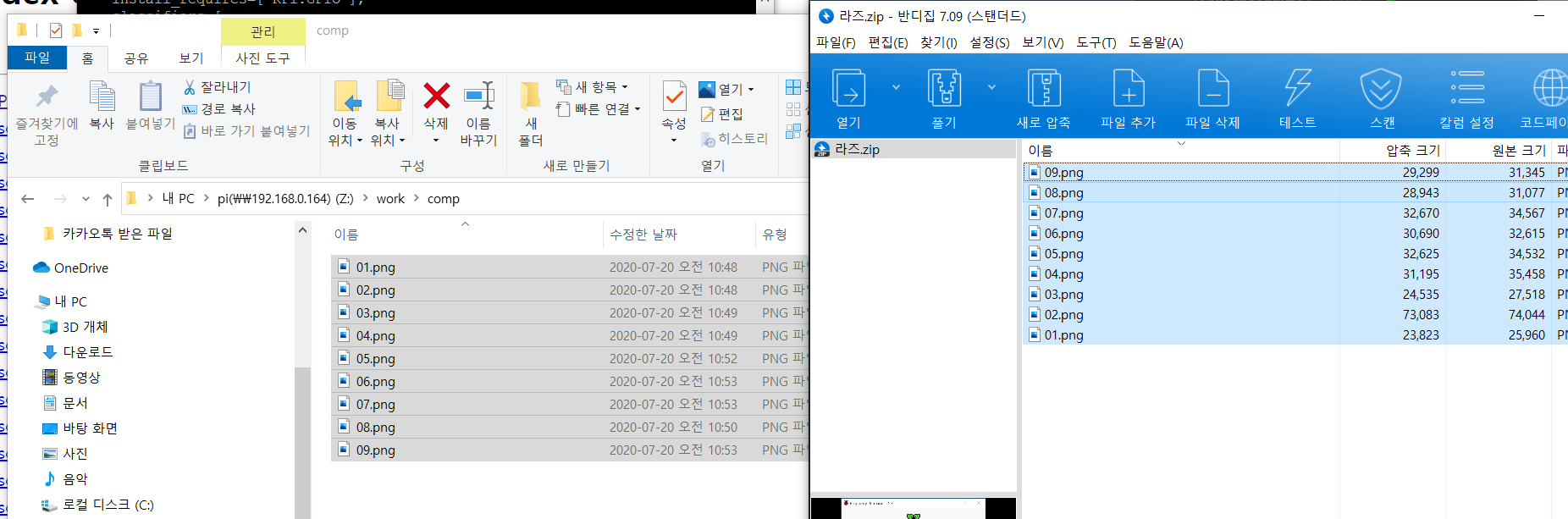

압축!
파일을 하나로 묶는 작업을 tar이라고 한다.
리눅스에서
한개씩 압축하는건 gzip이라고 한다. 개별 압축
tar -cf 한개로 묶는거 +묶는이름 추가
tar -cf auto.tar // 하나하나 따로 다 적어도 되는데 안적으면 한꺼번에 압축
*쓰면된다.

하나로 묶어주는 거지 용량 압축을 해주는 것은 아니다

용량 압축을 해주는 건 gzip auto.tar

다시 압축을 푸는 방법
gzip -d auto.tar.gz

지우기 rm *png

-v
혹은
--verbose
진행되는 파일의 이름을 화면에 출력함
보통 진행사항을 알 수 있기 때문에 사용
tar -xvf auto.tar
f는 파일
x는 풀때
v 표시
c 생성

rm auto.tar

한방에 압축하기

압축 만드는 예제

압축 푸는 예제






python tab +tab -> 파이선 명령어



vi 편집기 공부시간 !

모드는 3개가 있다
명령모드
명령어 입력모드
메모장 모드(편집모드)
항상 명령 모드를 거친다 !
esc 디폴트 esc
메모장 편집 모드 -> 명령 모드 <- 명령어 입력모드
메모장 편집 모드 <- 명령 모드 -> 명령어 입력모드
i 키사용
a키사용
o키사용
r키 사용


Alt키를 누르고 긁으면 내용만

w 키를 누를때 명령문 모드로 단어 단어로 점프한다!
$ 는 맨 뒤로
0 은 맨 앞으로
H 왼쪽
J 아래
K 위
L 오른쪽
DD -> 삭제
U -> 다시 살리기
P -> 붙여넣기
D +W 단어 하나만 삭제
D + 숫자 + 방향키 EX 숫자 2를 입력하고 방향키 아래로: 커서가 있는 줄 +2줄 삭제 총 3줄 삭제
SHIFT P는 위로 붙여주고
소문자 p는 아래로 붙여준다. 잘래낸것을
v 비주얼 이 켜진다. 방향키로 드레그 가능
shift +d -> 시작부터 해당 라인 전부 삭제
i(nsert) - 끼워넣기
w(ord) - 띄어쓰기 단위로 이동
u - 취소
$ - 줄 맨 뒤로
0 - 줄 맨 앞으로
d(elete) - 삭제
D - 현재 위치부터 끝까지 삭제
d + w - 한 단어단위 삭제
d + d - 잘라내기
d + 2 + k or j(방향키) - 위 or 아래로 2줄 삭제
p(소문자) - 붙여넣기(아래)
P(대문자) - 붙여넣기(위로)
h j k l - 방향
v(isual) + 방향키 = 드래그
v + d = 범위 삭제(잘라내기)
y -카피의 약자
x 한글자 삭제
몽땅 지울 때 d +99999 + 방향키 아래로
아래로 싹다 지워진다.
ctrl + r -> 다시 살시는거
y(소문자) = 한글자 copy
Y(대문자) = 한 줄 copy
x = 한글자 삭제
d + 999999 + k or j = 현위치부터 원하는 방향으로 전체 삭제
/-> search 역할
esc 디폴트 esc
메모장 편집 모드 -> 명령 모드 <- 명령어 입력모드
메모장 편집 모드 <- 명령 모드 -> 명령어 입력모드
i 키사용
a키사용
o키사용
r키 사용
정재민(교육), [23.07.20 15:17]
y(소문자) = 한글자 copy
Y(대문자) = 한 줄 copy
x = 한글자 삭제
d + 999999 + k or j = 현위치부터 원하는 방향으로 전체 삭제
정재민(교육), [23.07.20 15:21]
u = undo(실행 취소)
ctrl + r = redo(다시 실행)
정재민(교육), [23.07.20 15:25]
i = 끼워넣기(오른쪽)
a = 끼워넣기(왼쪽)
정재민(교육), [23.07.20 15:28]
o(소문자) = 새로운 줄 삽입(아래로)
O(대문자) = 새로운 줄 삽입(위로)
r + 다른 키 -> 바뀐다.
R -> 바꾸기 모드 다 덮어쓴다.

a=123
print(type(a))
a = 100*100
print(a)
a,b =9,2
print(a*b)
a = "파이썬 만세"
print(a)
print(type(a))
b ='python go'
print(b)
a,b,c,d, =0,0,0,0
hap = 0
a = int(input("1번째 숫자 : "))
b = int(input("2번째 숫자 : "))
c = int(input("3번째 숫자 : "))
d = int(input("4번째 숫자 : "))
hap = a+b+c+d
print("합계 ==> %d" %hap)
aa =[0,0,0,0]
aa[0] = int(input("1번째 숫자 : "))
aa[1] = int(input("2번째 숫자 : "))
aa[2] = int(input("3번째 숫자 : "))
aa[3] = int(input("4번째 숫자 : "))
hap = aa[0] +aa[1]+aa[2]+aa[3]
print("합계2 ==>%d"%hap)
aa =[]
aa.append(0)
print(len(aa))
print(aa)
bb =[]
for x in range(0, 100):
bb.append(x)
print(bb)
a=123
print(type(a))
a = 100*100
print(a)
a,b =9,2
print(a*b)
a = "파이썬 만세"
print(a)
print(type(a))
b ='python go'
print(b)
a,b,c,d, =0,0,0,0
hap = 0
a = int(input("1번째 숫자 : "))
b = int(input("2번째 숫자 : "))
c = int(input("3번째 숫자 : "))
d = int(input("4번째 숫자 : "))
hap = a+b+c+d
print("합계 ==> %d" %hap)
aa =[0,0,0,0]
aa[0] = int(input("1번째 숫자 : "))
aa[1] = int(input("2번째 숫자 : "))
aa[2] = int(input("3번째 숫자 : "))
aa[3] = int(input("4번째 숫자 : "))
hap = aa[0] +aa[1]+aa[2]+aa[3]
print("합계2 ==>%d"%hap)
aa =[]
aa.append(0)
aa.append(0)
aa.append(0)
aa.append(0)
print(len(aa))
print(aa)
bb =[]
for i in range(0,100):
bb.append(i)
print(bb)
갑자기 다시 C#
델리게이트 공부할 거임
using System;
class Program
{
static int OnePluse(int num)
{
return num + 1;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int TestNum = OnePluse(100);
Console.WriteLine(TestNum);
}
}
using System;
class Program
{
delegate int NewType(int num); // 새로 만든 뉴 타입 -> 클래스라고 생각하면 된다.
// 위임 = 대리자
//메소드를 가르키는 타입
static int OnePluse(int num)
{
return num + 1;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int TestNum = OnePluse(100);
Console.WriteLine(TestNum);
NewType anewType = new NewType(OnePluse); //메소드에 별칭을 달아주는 용도
TestNum = anewType(1000); //델리게이트를 쓰면 반복문을 쓸 수 있다.
Console.WriteLine(TestNum);
}
}
델리게이트
using System;
class Program
{
delegate int NewType(int num); // 새로 만든 뉴 타입 -> 클래스라고 생각하면 된다.
// 위임 = 대리자
//메소드를 가르키는 타입
static int OnePluse(int num)
{
return num + 1;
}
static int TenPluse(int num)
{
return num + 10;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int TestNum = OnePluse(100);
Console.WriteLine(TestNum);
NewType anewType = new NewType(OnePluse); //메소드에 별칭을 달아주는 용도
TestNum = anewType(1000); //델리게이트를 쓰면 반복문을 쓸 수 있다.
Console.WriteLine(TestNum);
anewType = new NewType(TenPluse);
TestNum = anewType(1000);
Console.WriteLine(TestNum);using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
delegate int Calculator(int v1, int v2);
private static int Sub(int v1, int v2)
{
return v1 - v2;
}
private static int Mul(int v1, int v2)
{
return v1 * v2;
}
private static int Div(int v1, int v2)
{
return v1 / v2;
}
private static int Add(int v1, int v2)
{
return v1 + v2;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int iresult
; Calculator[] calculator = new Calculator[] {Add,Sub,Mul,Div };
for (int i = 0; i < calculator.Length; i++)
{
iresult= calculator[i](3, 4);
Console.WriteLine(iresult);
}
foreach (var item in calculator)
{
iresult = item(3, 4);
Console.WriteLine(iresult);
}
for (int i = 0; i < calculator.Length; i++)
{
iresult = calculator[i](3, 4);
Console.WriteLine(iresult);
}
iresult = Add(3, 4);
Console.WriteLine(iresult);
iresult = Div(3, 4);
Console.WriteLine(iresult);
iresult = Sub(3, 4);
Console.WriteLine(iresult);
iresult = Mul(3, 4);
Console.WriteLine(iresult);
}
}
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp3
{
public class Mathematics
{
delegate int CalcDelegate(int x, int y);
static int Add(int x, int y) { return x + y; }
static int Sub(int x, int y) { return x - y; }
static int Mul(int x, int y) { return x * y; }
static int Div(int x, int y) { return x / y; }
CalcDelegate[] methods;
public Mathematics()
{
methods = new CalcDelegate[] { Mathematics.Add,Mathematics.Sub, Mathematics.Mul,Mathematics.Div};
}
public void Calculate(char opCode, int operand1, int oprand2)
{
switch (opCode)
{
case '+':
Console.WriteLine("+: " + methods[0](operand1,oprand2));
break;
case '-':
Console.WriteLine("-: " + methods[1](operand1, oprand2));
break;
case '*':
Console.WriteLine("*: " + methods[2](operand1, oprand2));
break;
case '/':
Console.WriteLine("/: " + methods[3](operand1, oprand2));
break;
}
}
class Program
{
delegate void WorkDelegate(char arg1, int arg2, int arg3);
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Mathematics mathematics = new Mathematics();
WorkDelegate workDelegate = mathematics.Calculate;
workDelegate('+', 10, 5);
workDelegate('-', 10, 5);
workDelegate('*', 10, 5);
workDelegate('/', 10, 5);
}
}
}
}
델리게이트를 더욱 쉽고 간단하게 하는건 내일 !
'Linux' 카테고리의 다른 글
| SMART FACTORY - 라즈베리파이에 온도 센서를 부착시켜보았다. /파이썬 -MySql DB연결 ! (0) | 2020.09.13 |
|---|---|
| SMART FACTORY -MYSQL /C# 데이터 베이스 연동 (0) | 2020.09.09 |
| SMART FACTORY - 뷰 함수 / HTML/ FLASK 웹서버 구축하기 (0) | 2020.07.28 |
| SMART FACTORY - PYTHON 을 조금 더 공부 해 볼깝쏘? / 오늘 수업 뒤죽 박죽이네 (0) | 2020.07.24 |
| SMART FACTORY - 리눅스 명령어 ! (0) | 2020.07.22 |
| SMART FACTORY 라즈베리파이 ! -리눅스 (0) | 2020.07.21 |



